
Neulog Galvanic Response Sensor Skin Changes According
This sensor has two ranges: conductivity in microsiemens and arbitrary numbers.Dental anxiety is a constant challenge for both the practitioner and patient that often impairs the ability of the dentist to deliver routine care. The conductivity of our skin changes according to unconscious emotion effects such as sudden noise, smell, touch, pain or view. Neulog Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) logger sensor measures the conductivity of our skin, especially of our fingers.
One study reported that the sight and sounds of the dental drill produces panic in some patients ( 3). Additionally, proprioceptive triggers such as smells, sounds, sight, and touch are a common source of fear ( 2). People also report the lack of understanding and a sense of vulnerably, specifically associated with lying in the supine position, as a cause for apprehension. Often stories portrayed through media or word of mouth convey a disturbing portrayal of dentistry.
Neulog, Pulse Logger Sensor. Blood Pressure Logger Sensor. It is exactly those changes that the Galvanic Skin Respon.NeuLog. This psychological fear can drive patients to avoid regular dental care as stated by Coriat “any dental surgery, no matter how minor, or even dental prophylaxis, may be so postponed or procrastinated that the inroads of disease may affect the entire dental apparatus ( 7).”NeuLog Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) Logger Sensor The tiniest emotional ripples we unconsciously experience affect our skins conductivity. Studies have shown that anxiety has a direct impact in decreasing the pain threshold, and has been implicated in elevating pain intensity ( 5, 6). All these nociceptive feelings can result in the creation of patients with the inability to cope with preventative care.
A range of distraction methods that are known to work in decreasing patient anxiety and thus perceived pain perception include music, audiovisual, and touch ( 9). In this method, pain perception is reduced due to the increased mental demand towards more pleasant stimuli ( 8). Cognitive refocusing is a method based on theory of pain where a distraction diverts pain perception by focusing attention to more amusing attractions. Contact Us Terms and Conditions Delivery and Returns Report a Website Issue CORPORATE. Neulog, Respiration Monitor Belt Logger Sensor.
Right side) were randomized per appointment visit. Using a random number generator, treatment (with/without squeeze balls) and order (left vs. The contralateral side (maxillary and mandibular) received Sc/RP with local anesthesia without the use of squeeze ball distraction (control group). (Fig.1) 1) distraction (Why Worry? Be Happy! Neon Yellow Funny Face Stress Ball, Neliblu, Seattle, WA, USA) at one of two appointments (experimental group). This study used a randomized “split-mouth” design with one side of the mouth (maxillary and mandibular) receiving Sc/RP with local anesthetic with the use of a squeeze ball (Fig.
STAI was originally established in 1970 as an assessment to allow patients to self-evaluate their current level of anxiety ( 14). (Fig.3) 3) before and after each procedure. (Fig.2) 2) and a Modified Dental Anxiety Scale (MDAS) (Fig. Subjects completed a six-item short form Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) (Fig.
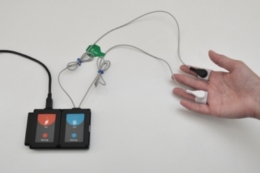
The long buccal nerve block injection was given between the distal mandibular alveolar crest and the external oblique ridge. The inferior alveolar nerve block injection was given at the pterygotemporal depression. The principle investigator performed the site injections to standardize the anesthetic flow rate and technique. Inferior alveolar and long buccal nerve block injections were administered for injections on the mandible and buccal infiltration injections were provided on the maxillary arch. Using a split-mouth design, the subjects served as their own control and a total of twenty subjects achieved a power of 80% to detect an 0.67 standard deviation difference or medium effect size for a two-sided test with a significance level of 0.05 (NCSS) PASS v.11.0.8, Kaysville, UT, USA.Velcro connectors were wrapped around two different fingers on the hand opposite the hand using the stress ball.A topical anesthetic (benzocaine 20% gel Topex, Sultan Healthcare, NJ, USA) was used to anesthetize the surface tissue at the sites receiving the injections for 2 minutes. The patient was instructed to squeeze the stress ball at any time during the procedure.
Sc/RP was performed using hand and ultrasonic scalers Piezon Master 700, Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA).Post treatment STAI and MDAS assessments were completed after every session. A new needle was used for each injection site to ensure a fresh, sharp cutting tip and to control for injection site pain. The anesthetic solution (2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine, Henry Schein, Melville, NY, USA) was administered using a 27-gauge long needle (Monoject, Covidien AG, Neuhausen am Rheinfall, Switzerland) for the mandibular injections and a 30-gauge short needle (Monoject) for the maxillary injections, with a standard dental anesthetic syringe.
The sum of all five items can range from 5-25, with a score of 11 – 14 considered moderate anxiety and over 15 considered high anxiety ( 15).A median and interquartile range was determined per group for GSR and before and after treatment for both STAI and MDAS. Evaluation of MDAS was completed using the MDAS Scale, where each item was scored from “not anxious” to “extremely anxious”, with an assigned numerical value from 1-5 respectively. According to Bekker et al., a score range of 34-36 is considered normal ( 17). All six scores are summed up and multiplied by 20 and divided by 6. Anxiety absent items (calm, relaxed, content) are reversed, and values marked as 1, 2, 3, 4 are scored as 4, 3, 2, 1 respectively. Anxiety items (tense, upset, worried) carry a normal scoring trend with a value of 4 indicating a high level of anxiety.
The continuous GSR data were analyzed with a Shapiro Wilk test and found to be not normally distributed. Additionally, subjects were asked after the second appointment to indicate whether they had preferred the first session, or the second session or if they had no preference between either sessions.The subject pool was made up of 15 males and 5 females with ages ranging from 24-85 years (mean 54 years). Data were evaluated using a Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test (alpha=0.5) with statistical software (SPSS, version 25, IBM, Armonk, NY). Also, the change in STAI and MDAS scores before and after treatment were determined for each group.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
